Home » DC Servo Motor » How Does DC Servo Motor Work?
How Does DC Servo Motor Work?
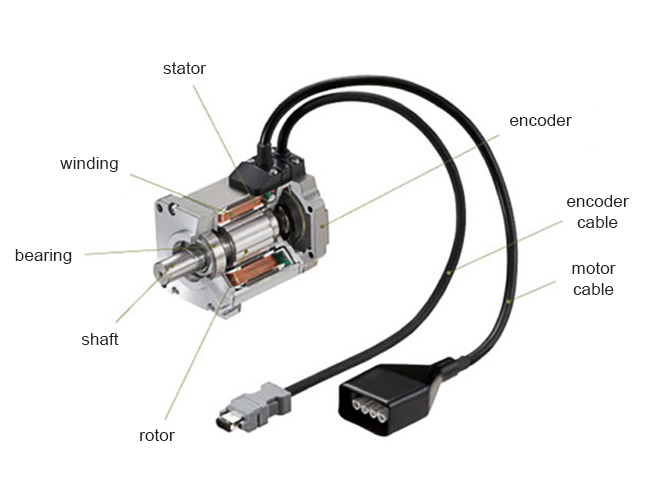
 A DC servo motor along with servomechanism (closed-loop control system) acts as a servo motor which is basically used as a mechanical transducer in the automation industry. Based on its accurate closed-loop control, it has versatile applications used in many industries. The DC servo motor definition is, a motor that is used in servo systems is known as a servo motor. A servo system is a closed-loop system where the feedback signal (position, velocity, acceleration, etc.) drives the motor. This signal acts as an error and based on controller, accurate position or velocity is achieved. The motors are coupled to an output shaft (load) through a gear train for power matching.
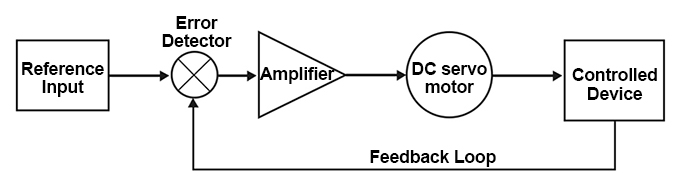
A DC servo motor along with servomechanism (closed-loop control system) acts as a servo motor which is basically used as a mechanical transducer in the automation industry. Based on its accurate closed-loop control, it has versatile applications used in many industries. The DC servo motor definition is, a motor that is used in servo systems is known as a servo motor. A servo system is a closed-loop system where the feedback signal (position, velocity, acceleration, etc.) drives the motor. This signal acts as an error and based on controller, accurate position or velocity is achieved. The motors are coupled to an output shaft (load) through a gear train for power matching.Servo motor acts as a mechanical transducer as they convert an electrical signal to an angular velocity or position. High precision DC servo motor working principle consider the following block diagram which consists of the different blocks where the name of each block is explained in brief. Motor It is a normal DC motor with its field winding separately excited. Based on the nature of excitation, it can be further classified as field controlled and armature controlled servo motors load It is connected to a mechanical shaft of the motor. It could be any industrial load or a simple fan load.
It acts like a proportional controller where the gain is amplified for zero steady-state error. Control signal and pulse width modulator based on the feedback signal, controlled gives the input to pulse width modulator which modulates the input of motor (voltage or field excitation) for exact control or zero steady-state error.
The pulse width modulator further uses a reference waveform and comparator to generate pulses. By making the system closed-loop exact position, acceleration or velocity is obtained. The name servo motor implies a controlled motor that gives the desired output because of the effect of feedback and controller. The error signal is amplified and used to drive the servo motor. Based on the nature of producing control signal and pulse width modulator, servo motors can have advanced controlled techniques using digital signal processors or FPGA chips. Characteristics of DC servo motor The characteristic or in other words the requirements of a servo motor are: The inertia of the servo motor should be less for precision and accuracy It should have a fast response which can be obtained by keeping high torque to weight ratio.
The torque-speed characteristics should be linear four quadrant operation is desirable by using further converters. Stable operation Robust nature. Types of DC servo motor based on the nature of electric supply servo motors can be classified as AC and DC servomotors. Again based on speed control, the DC servomotors can be classified as armature controlled and field controlled servomotors.
Let Ra= Armature Resistance La = Armature Inductance Ia = Armature Current Va = Armature Voltage Wm = Angular Velocity Eb = Back EMF J = Moment of Inertia If = Field Current Lf = Field Inductance Tm = Torque Produced Eb = Back EMF produced by the motor Applying KCL in the armature we get Va = ia Ra + La *(dia/dt) + eb The load torque equation is given by J * (d2 θ/dt2) + B * (dθ/dt) = Tm = K1 ia Substituting i_a in the second equation and converting into the Laplace domain, the transfer function of the DC servomotor can be obtained as below:
Post a Comment:
You may also like:
Category
Featured Articles
What is a Servo Motor?
 There are some special types of application of electrical motor where rotation of the motor is required for just a certain angle ...
There are some special types of application of electrical motor where rotation of the motor is required for just a certain angle ...
 There are some special types of application of electrical motor where rotation of the motor is required for just a certain angle ...
There are some special types of application of electrical motor where rotation of the motor is required for just a certain angle ...What are the Basics of Servo Drive?
 Servo motors come in so many types and flavors that it is difficult to define them in a way that is accurate and universally ...
Servo motors come in so many types and flavors that it is difficult to define them in a way that is accurate and universally ...
 Servo motors come in so many types and flavors that it is difficult to define them in a way that is accurate and universally ...
Servo motors come in so many types and flavors that it is difficult to define them in a way that is accurate and universally ...Why Use Servo Motor as Test Load?
 Dynamometer is mainly divided into two parts: cabinet and frame, while the frame mainly has the motor under test, torque speed ...
Dynamometer is mainly divided into two parts: cabinet and frame, while the frame mainly has the motor under test, torque speed ...
 Dynamometer is mainly divided into two parts: cabinet and frame, while the frame mainly has the motor under test, torque speed ...
Dynamometer is mainly divided into two parts: cabinet and frame, while the frame mainly has the motor under test, torque speed ...What Should Consider Before Using ...
 Servo system is a commonly used control system, widely used in industrial automation. It compares the output signal with the ...
Servo system is a commonly used control system, widely used in industrial automation. It compares the output signal with the ...
 Servo system is a commonly used control system, widely used in industrial automation. It compares the output signal with the ...
Servo system is a commonly used control system, widely used in industrial automation. It compares the output signal with the ...Servo Motor in Food Industry
 In the ever-evolving landscape of the food industry, technological advancements play a pivotal role in enhancing efficiency, ...
In the ever-evolving landscape of the food industry, technological advancements play a pivotal role in enhancing efficiency, ...
 In the ever-evolving landscape of the food industry, technological advancements play a pivotal role in enhancing efficiency, ...
In the ever-evolving landscape of the food industry, technological advancements play a pivotal role in enhancing efficiency, ...