Home » Servo Drive
ATO suppliers provide servo drives. Servo drive, also known as a servo controller, is a controller used to control servo motors. Three-phase 220V AC servo drivers are mainly used in high-voltage applications and precise positioning systems, it is widely used in industrial robots, CNC machining centers, and other automation equipment. The servo driver with innovation design can perform short-distance rapid positioning operations and is easy to operate.
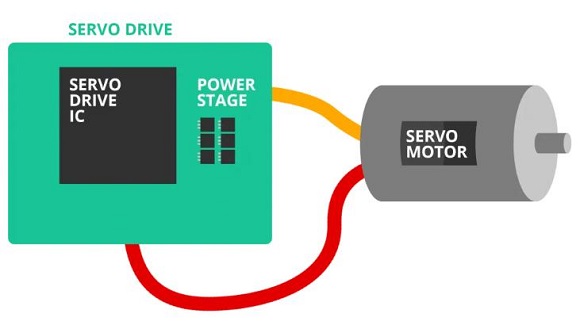
Servo motors come in so many types and flavors that it is difficult to define them in a way that is accurate and universally acceptable. It is possible, though, to describe some of the things commonly found in servo drives, as well as typical configurations. Servo drives are designed to convert electrical power into precision controlled motion, controlled torque (torque servo), controlled speed (velocity servo) or controlled position (positioning servo). This typically requires at least three elements: the motor, feedback of some sort, and an amplifier.
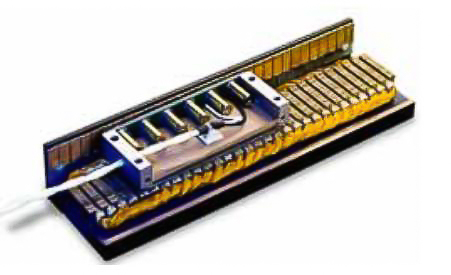

Servo drive is an indispensable andimportant component of modern industrial automation system, and its normaloperation has an important impact on the stability and productivity of theproduction line and production efficiency has an important impact. However, dueto a variety of factors, the servo drive may appear a variety of failures. In order to ensure the stable operation ofthe servo drive, we need to take a series of measures to prevent and solve theproblem. In this article, we will discuss the common servo drive failures, howto prevent and solve servo drive failures and other topics.
Servo drive to achieve high-precisionpositioning mainly depends on its closed-loop control system and relatedtechnology. The following are some key points.
- Encoder feedback: servo motors areequipped with high-resolution encoder, which can provide real-time position andspeed of the motor feedback.
- Controller algorithms: Themicrocontroller in the servo drive adjusts the motor's input voltage or currentaccording to the encoder feedback and controller algorithms to control themotor's speed and position.
- Current and speed closed-loop control:servo drive with current and speed closed-loop control, can quickly respond tospeed changes or load disturbances, to ensure that the motor to run in the beststate.
- Position control: through the controlleralgorithm, the servo drive can accurately control the position of the motor,even in complex trajectories or rapid positioning applications can alsomaintain high accuracy.
- Rigidity: the rigidity of the servo driveand motor system determines its resistance to external disturbances (such asload changes). High rigidity can ensure that in high-precision positioningapplications, even in external interference, the system can remain stable.
- Control strategy: servo drive can use avariety of advanced control strategies, such as adaptive control, fuzzycontrol, in order to improve the dynamic performance of the system andpositioning accuracy.
- Temperature compensation: servo driveusually has a temperature compensation function to reduce the motor due totemperature changes and thermal errors, further improve positioning accuracy.
Modern AC servo drives, depending on the end application, need high-bandwidth current control and speed control to enable superior performance, such as in CNC machines or in fast and precision control applications. With the Microcontroller unit (MCU), due to its higher level of integration, it is possible to implement fast current loop (FCL) algorithms that provide a high current loop bandwidth with the same external hardware as used in classical Field-Oriented Control methods.
Servos (as commonly used in radio-controlled vehicles and small-scale robotics)are DC actuators that use a potentiometer to provide built in feedback to localize an actuator arm. To minimize jerky control movements, many servo controllers include velocity and acceleration control which operate using a defined velocity profile resulting in the Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) control value being changed over time.
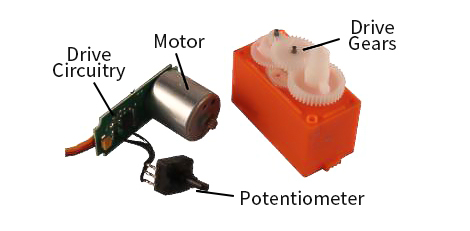
On power-up, the initial position of the servoarm is unknown to the external controller-resulting in the arm moving to the starting value at maximum speed (which may be mechanically hazardous). In this paper, two different techniques for performing a soft-start for servos are described and evaluated, namely: voltage profiling and intermittent drive.

On power-up, the initial position of the servoarm is unknown to the external controller-resulting in the arm moving to the starting value at maximum speed (which may be mechanically hazardous). In this paper, two different techniques for performing a soft-start for servos are described and evaluated, namely: voltage profiling and intermittent drive.
Installing a servo drive involves several steps, and the specific process may vary depending on the manufacturer and model of the servo drive you're working with. However, I can provide you with a general guide on how to install a servo drive. Keep in mind that this is a basic overview, and you should always refer to the manufacturer's documentation for detailed and accurate instructions. Also, ensure that you follow safety guidelines and, if necessary, consult with a qualified technician.
Such as read the documentation, mounting, connect power supply and motor connection and so on. These steps are general guidelines, and the actual installation process may vary. Always refer to the manufacturer's documentation for specific details and instructions related to your servo drive model. If you are unsure with the installation process, consider seeking assistance from a qualified technician or contacting the manufacturer's support.

Such as read the documentation, mounting, connect power supply and motor connection and so on. These steps are general guidelines, and the actual installation process may vary. Always refer to the manufacturer's documentation for specific details and instructions related to your servo drive model. If you are unsure with the installation process, consider seeking assistance from a qualified technician or contacting the manufacturer's support.
Safety precautions are essential when working with servo drives to ensure the well-being of personnel and the proper functioning of equipment. Here are some general safety precautions to consider.
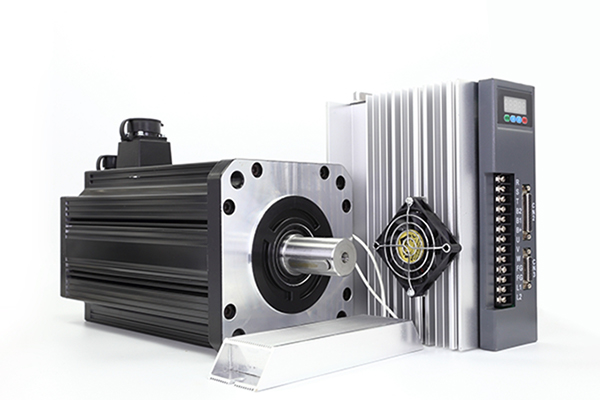
A servo drive system, as opposed to a variable frequency drive (VFD) or AC motor drive , has the ability to position with extreme precision and repeatability. While a VFD can be configured for position control, it cannot attain the exactness of a servo drive. VFDs are also available in much higher horsepower ranges than servo's. Selection of external feedback sensors such as encoders, resolvers, linear position sensors, etc., required to achieve closed-loop control and each having its own inherent precision, will enable the system accuracy accordingly. Your application requirements will always dictate which system configuration will give you the best results. Many of today's VFDs are fully capable of doing positioning when using encoder feedback; as with many other things, the lines have become blurred. What separates servo motor from induction motors is their low inertia and their ability to accelerate and decelerate much faster, the trick is to decide when you need full servo performance.


Category
Featured Articles
What are the Basics of Servo Drive?
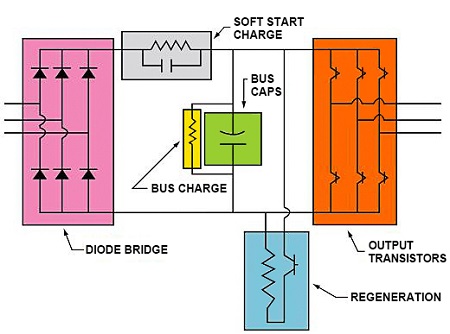 Servo motors come in so many types and flavors that it is difficult to define them in a way that is accurate and universally ...
Servo motors come in so many types and flavors that it is difficult to define them in a way that is accurate and universally ...
 Servo motors come in so many types and flavors that it is difficult to define them in a way that is accurate and universally ...
Servo motors come in so many types and flavors that it is difficult to define them in a way that is accurate and universally ...What are the Soft Start Techniques for ...
 Servos (as commonly used in radio-controlled vehicles and small-scale robotics)are DC actuators that use a potentiometer to ...
Servos (as commonly used in radio-controlled vehicles and small-scale robotics)are DC actuators that use a potentiometer to ...
 Servos (as commonly used in radio-controlled vehicles and small-scale robotics)are DC actuators that use a potentiometer to ...
Servos (as commonly used in radio-controlled vehicles and small-scale robotics)are DC actuators that use a potentiometer to ...How to Install a Servo Drive?
 Installing a servo drive involves several steps, and the specific process may vary depending on the manufacturer and model of the ...
Installing a servo drive involves several steps, and the specific process may vary depending on the manufacturer and model of the ...
 Installing a servo drive involves several steps, and the specific process may vary depending on the manufacturer and model of the ...
Installing a servo drive involves several steps, and the specific process may vary depending on the manufacturer and model of the ...Servo Drive System vs. Variable ...
 A servo drive system, as opposed to a variable frequency drive (VFD) or AC motor drive , has the ability to position with ...
A servo drive system, as opposed to a variable frequency drive (VFD) or AC motor drive , has the ability to position with ...
 A servo drive system, as opposed to a variable frequency drive (VFD) or AC motor drive , has the ability to position with ...
A servo drive system, as opposed to a variable frequency drive (VFD) or AC motor drive , has the ability to position with ...